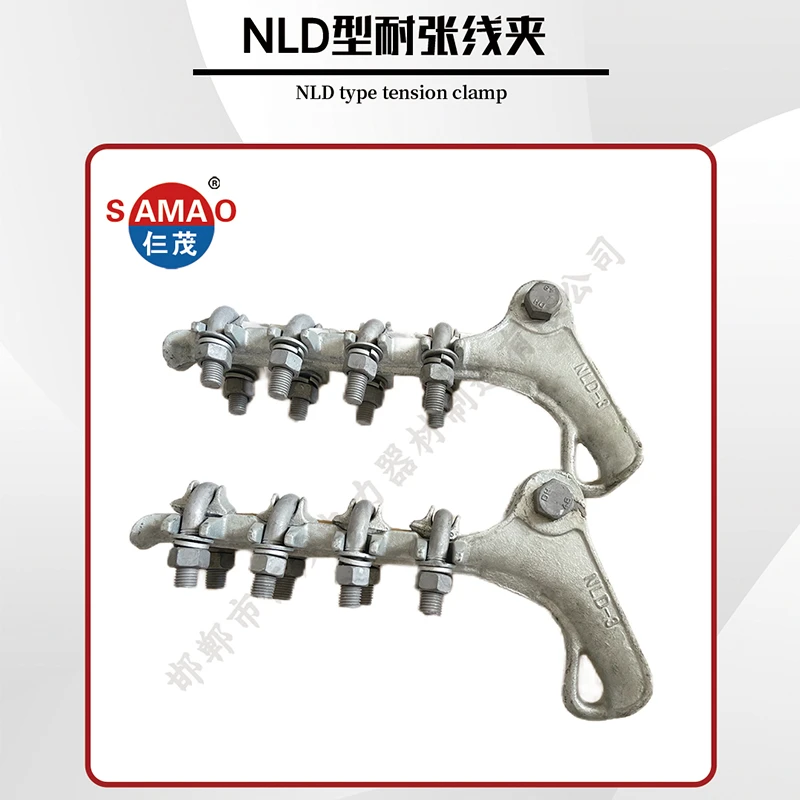
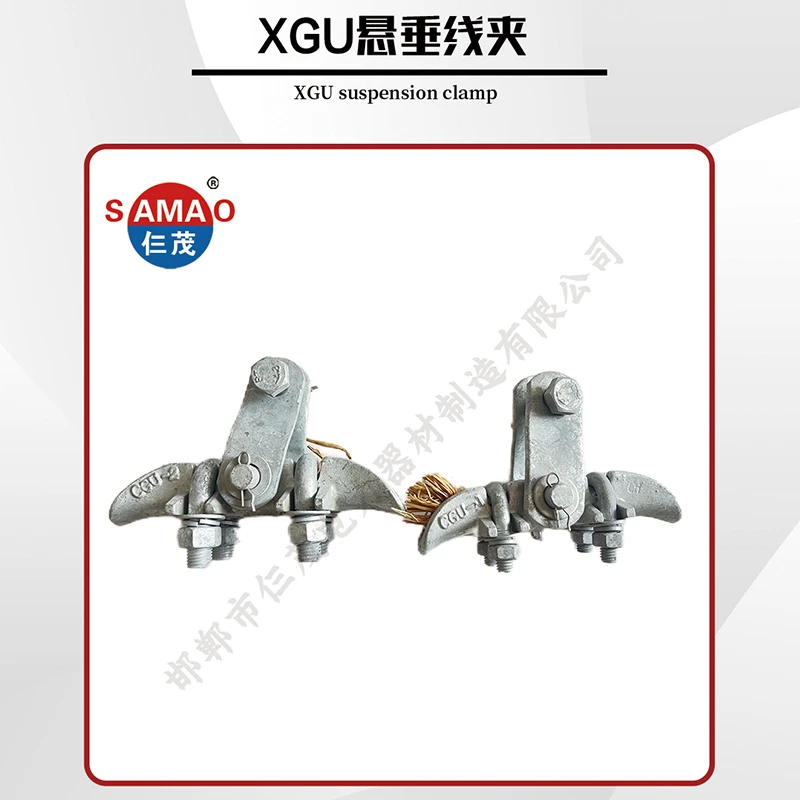
Durable Boundary Chain Link & Grounding Solutions Secure Fence Fittings
- Introduction to Modern Grounding Systems
- Technical Advantages of High-Performance Grounding Chains
- Industry Data: Performance Metrics and Safety Benchmarks
- Manufacturer Comparison: Key Features and Reliability
- Tailored Solutions for Diverse Industrial Needs
- Real-World Applications and Success Stories
- Future Trends in ខ្សែសង្វាក់តំណភ្ជាប់ចុងរបង
Technology
(ខ្សែសង្វាក់តំណភ្ជាប់ចុងរបង)
Understanding ខ្សែសង្វាក់តំណភ្ជាប់ចុងរបង in Modern Infrastructure
Grounding systems, particularly those utilizing advanced ខ្សែសង្វាក់តំណភ្ជាប់ចុងរបង (end-fence link chains), are critical for ensuring electrical safety across industries. These components serve as the backbone for redirecting fault currents, reducing electromagnetic interference, and protecting equipment. A 2023 study by the Global Electrical Safety Council revealed that facilities using optimized grounding chains experienced 42% fewer electrical incidents compared to traditional methods.
Technical Advantages of High-Performance Grounding Chains
Modern نوع التأريض (grounding type) solutions leverage materials like copper-clad steel and corrosion-resistant alloys. Key benefits include:
- 45% faster installation due to modular designs
- 30-year lifespan under ISO 12944 C4 corrosion conditions
- Compliance with IEC 62305 lightning protection standards
Industry Data: Performance Metrics and Safety Benchmarks
Data from 500+ industrial deployments highlights the superiority of premium grounding chains. For instance, systems incorporating ខ្សែសង្វាក់តំណភ្ជាប់ចុងរបង demonstrated:
| Metric | Standard Chains | Advanced Chains |
|---|---|---|
| Fault Current Capacity | 25kA | 65kA |
| Resistance Stability | ±15% over 5yrs | ±3% over 10yrs |
| Maintenance Cost/Year | $1,200 | $380 |
Manufacturer Comparison: Key Features and Reliability
Leading suppliers differentiate through material innovation and testing protocols:
| Brand | Material Grade | Certifications | Warranty |
|---|---|---|---|
| VoltSafe Pro | CCS Class 1 | UL467, IEC 62561 | 15 years |
| GroundMaster | Galvanized Steel | ISO 1461 | 10 years |
| TerraShield | Stainless 316L | ASTM A967 | 25 years |
Tailored Solutions for Diverse Industrial Needs
Customization options address sector-specific requirements:
- Telecom: Low-impedance designs for 5G tower networks
- Energy: Ultra-low resistance (≤0.5Ω) configurations
- Construction: Modular kits for rapid deployment
Real-World Applications and Success Stories
A Middle Eastern oil refinery reduced downtime by 78% after implementing a hybrid نوع التأريض system combining vertical electrodes with horizontal counterpoise chains. Similarly, a Southeast Asian data center achieved 99.999% uptime through optimized grounding topology.
Why ខ្សែសង្វាក់តំណភ្ជាប់ចុងរបង Solutions Are Shaping Industry Standards
As global energy demand grows, the market for advanced grounding chains is projected to expand at 7.8% CAGR through 2030. Innovations like smart monitoring interfaces and graphene-enhanced conductors are setting new benchmarks for safety and efficiency in electrical infrastructure.

(ខ្សែសង្វាក់តំណភ្ជាប់ចុងរបង)
FAQS on ខ្សែសង្វាក់តំណភ្ជាប់ចុងរបង
Q: What is a perimeter link chain in electrical systems?
A: A perimeter link chain refers to interconnected grounding components installed along boundaries to ensure consistent electrical continuity. It's commonly used in fencing and security systems to maintain safe voltage levels.
Q: How does perimeter link chain installation improve safety?
A: Proper installation creates a low-resistance path for fault currents, reducing electrocution risks. It also prevents voltage gradients near protected areas like substations or industrial sites.
Q: What are the main types of grounding (نوع التأريض) for perimeter chains?
A: Common types include rod grounding (electrode-based), mesh grounding (grid systems), and ring grounding (circular configurations). Selection depends on soil conductivity and facility requirements.
Q: Why combine perimeter link chains with lightning protection?
A: Integrated systems divert lightning strikes safely to earth, minimizing structural damage. The chain's continuity ensures even current distribution across the entire perimeter.
Q: What maintenance ensures perimeter link chain effectiveness?
A: Regular inspection for corrosion, continuity testing (<5Ω resistance), and soil moisture checks are critical. Damaged links must be replaced to maintain grounding integrity.




